Dfs Using Stack In C

Next we visit the element at the top of stack i e.
Dfs using stack in c. Stack emplace in c stl. There is an alternate way to implement dfs. Insert the root in the stack. Using recursion and without recursion.
Do you really need to see stack vertext stack new stack vertex in order to figure out that stack is a stack of vertices. This can be designated as dfs g v. In your depth first search dfs program in c adjacency list code the loop on line 57 looks wrong. You initialize g 0 to null and then begin inserting all the edges before you finish initializing the rest of g.
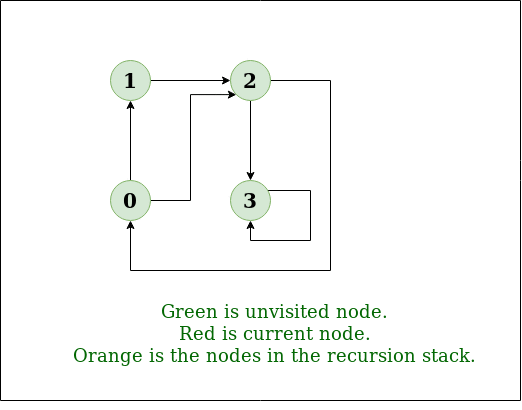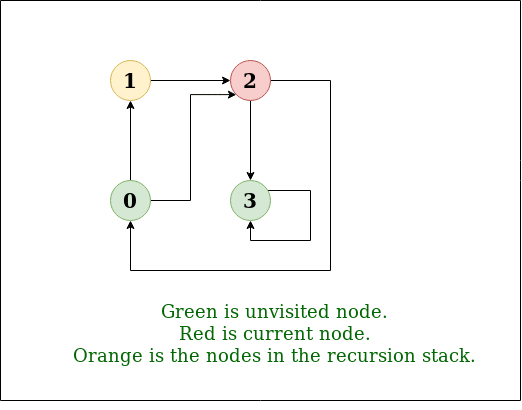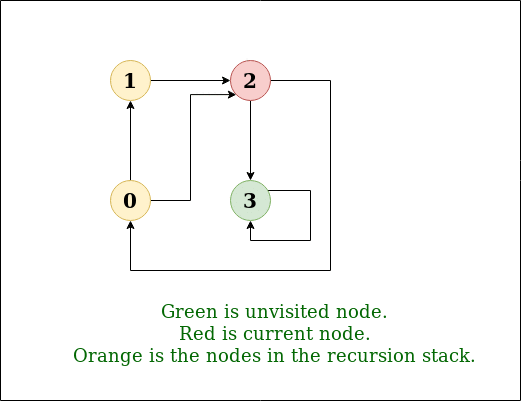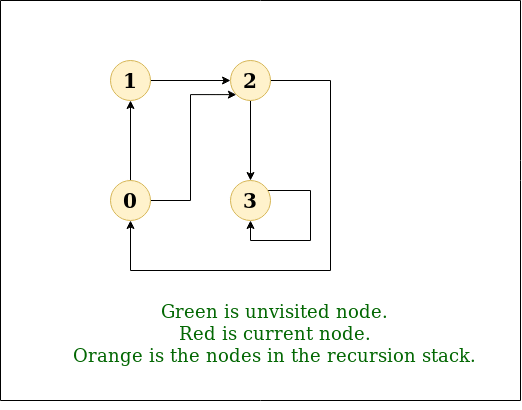
C programming flowcharts java programming cpp html css java script competitive programming tutorials. The compiler doesn t need my help. Undirected graph with 5 vertices. We start from vertex 0 the dfs algorithm starts by putting it in the visited list and putting all its adjacent vertices in the stack.
Since you use the variable i for both loops you win not continue where you left off which doesn t matter since you. The non recursive implementation of dfs is similar to the non recursive implementation of bfs but differs from it in two ways. The question of whether or not to use var in this case is whether the humans need help figuring it out. Depth first search dfs implementation using c programming9.
Since stack uses first in last out approach to handle elements. We will add the adjacent child nodes of a parent node to the stack. Sort a stack using recursion. 1 and go to its adjacent nodes.
Detecting cycles in the graph. If we find a back edge while performing dfs in a graph then we can conclude that the graph has a cycle hence dfs is used to detect the cycles in a graph. Check if the elements of stack are pairwise sorted. Stack of pair in c stl with examples.
Visit the element and put it in the visited list. Delete middle element of a stack. The generates of first element should be placed at the top of stack. Level order traversal in.
V labeled as discovered are assumed to be output. The only difference between iterative dfs and recursive dfs is that the recursive stack is replaced by a stack of nodes. Sudo placement 1 3 stack design. Go back to step 2.
Dfs using stack. In this approach we will use stack data structure. There are two ways of presenting the pseudo code for dfs. Stack unwinding in c.
Consider a graph g with vertex v. Created a stack of nodes and visited array. Given two vertices x and y we can find the path between x and y using dfs we start with vertex x and then push all the vertices on the way to the stack till we encounter y. It knows what the data type is.
Pop the element from the stack and print the element. It uses reverse iterator instead of iterator to produce same results as recursive dfs. Run a loop till the stack is not empty. We use an undirected graph with 5 vertices.